If the conversion mode is set to High Speed, the AcroPDF options would appear. For more information on AcroPDF options, read http://www.acropdf.com/manual.pdf.
If the conversion mode is set to High Quality, and once this button is clicked, you will see the following dialog,
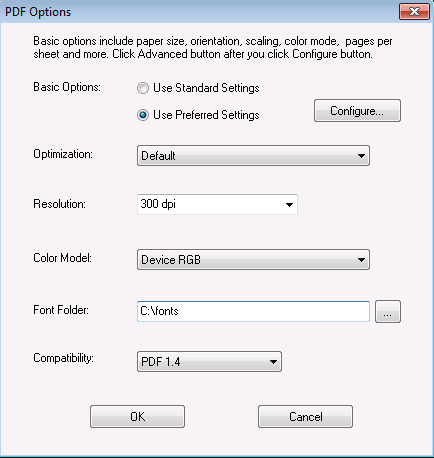
All the settings in this dialog are for the generation of PDF files. Before you adjust the settings, you are required to set the Basic Options to Use Predefined Settings.
Optimization: Decide what you want the output PDF file to be. For example, you want it to be viewed on screen, be printed, or for prepress purpose.
Resolution: Define the resolution of your PDF document in DPI. Usually, it's 200 DPI or 300 DPI.
Color Model: Specify which color model should be followed to process images and graphics in your AFP documents and get them converted to PDF. It can be Device RGB, Device CMYK, or Device Gray.
Font Folder: You can add fonts to the PDF to AFP transforms, which allows you to print documents with fidelity when the needed font is on your system. Here you can specify the font folder. If you wish to include multiple font folders, use semi comma as the separator. For example, c:\gs\fonts;c:\fontlib
AFM and PFB fonts are supported fonts, you can get the most commonly used fonts package from,
http://sourceforge.net/projects/gs-fonts/
Compatibility: Regulate the output PDF version. PDF 1.2 is a relatively low version, supported by Adobe Acrobat and Adobe Reader 3.0 or higher. PDF 1.6 is a relatively high version, supported by Adobe Acrobat and Adobe Reader 7.0 or higher.